Protein expression services for Zfp36l2 | mRNA decay activator protein ZFP36L2
Description
Zinc-finger RNA-binding protein that destabilizes several cytoplasmic AU-rich element (ARE)-containing mRNA transcripts by promoting their poly(A) tail removal or deadenylation, and hence provide a mechanism for attenuating protein synthesis (PubMed:22701344, PubMed:22367205, PubMed:25505318, PubMed:24830504, PubMed:27102483). Acts as a 3'-untranslated region (UTR) ARE mRNA-binding adapter protein to communicate signaling events to the mRNA decay machinery (By similarity). Functions by recruiting the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex and probably other components of the cytoplasmic RNA decay machinery to the bound ARE-containing mRNAs, and hence promotes ARE-mediated mRNA deadenylation and decay processes (By similarity). Binds to 3'-UTR ARE of numerous mRNAs (PubMed:22701344, PubMed:22367205, PubMed:25505318, PubMed:24830504). Promotes ARE-containing mRNA decay of the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor (LDLR) mRNA in response to phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) treatment in a p38 MAPK-dependent manner (By similarity). Positively regulates early adipogenesis by promoting ARE-mediated mRNA decay of immediate early genes (IEGs) (PubMed:22701344). Plays a role in mature peripheral neuron integrity by promoting ARE-containing mRNA decay of the transcriptional repressor REST mRNA (PubMed:25505318). Plays a role in ovulation and oocyte meiotic maturation by promoting ARE-mediated mRNA decay of the luteinizing hormone receptor LHCGR mRNA (PubMed:24830504). Acts as a negative regulator of erythroid cell differentiation: promotes glucocorticoid-induced self-renewal of erythroid cells by binding mRNAs that are induced or highly expressed during terminal erythroid differentiation and promotes their degradation, preventing erythroid cell differentiation (PubMed:19633199, PubMed:23748442). In association with ZFP36L1 maintains quiescence on developing B lymphocytes by promoting ARE-mediated decay of several mRNAs encoding cell cycle regulators that help B cells progress through the cell cycle, and hence ensuring accurate variable-diversity-joining (VDJ) recombination process and functional immune cell formation (PubMed:27102483). Together with ZFP36L1 is also necessary for thymocyte development and prevention of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) transformation by promoting ARE-mediated mRNA decay of the oncogenic transcription factor NOTCH1 mRNA (PubMed:20622884).
Species
Mus musculus
Length
484 amino acids
Sequence
MSTTLLSPFYDIDFLCKTEKSLANLNLNNMLDKKAVGTPVAAAPSSSFTPGFLRRHSASNLHALAHPVPSPGSCSPKFPGAPNGGGSSCGPAGGGGLASYGQLKEPSGGSGTALVTKESKFRDRSFSENGERSQHLLHLQQQQKGGSGSQINSTRYKTELCRPFEESGTCKYGEKCQFAHGFHELRSLTRHPKYKTELCRTFHTIGFCPYGPRCHFIHNADERRPAPSGGGGASGDLRAFGARDALHLGFAREPRPKLHHSLSFSGFPSGHHQPPGGLESPLLLDSPTSRTPPPPSSSASSCSSSASSCSSASAASTPSGAPTCCATAAAAALLYGPGGAEDLLSPGAPCASCSSSGANNAFAFGPELSSLITPLAIQTHNFAAAAAAAYYRNQQQGLTGPAPPPAQPPAAPAPPSPPFGFQLPRRLSESPVFDAPPSPPDSLSDRDSYLSGSLSSGSLSGSESPSLDPGRRLPIFSRLSISDD
Mass
50.1 kDa
Simulated SDS-PAGE
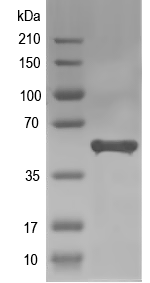 (Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)
(Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)Safety
Upon ordering, we will perform rigorous biosecurity and export control screening to ensure that order fulfillment is consistent with all legal and regulatory guidance.
Protein synthesis service
Make Zfp36l2 using our protein expression services starting at $99 + $.30/amino acid in as fast as two weeks (includes the cost of DNA synthesis)
Order Here