Protein expression services for tfs | Transcription factor S
Description
Induces RNA cleavage activity in the RNA polymerase. In its presence, the cleavage activity of the RNA polymerase truncates the RNA back to position +15 in a stepwise manner by releasing mainly dinucleotides from the 3'-end of the nascent RNA. The truncated RNAs are able to continue elongation. Involved in transcriptional proofreading and fidelity. Misincorporation of nucleotides during elongation of transcription leads to arrested elongation complexes which are rescued by TFS-promoted removal of a dinucleotide from the 3'-end. TFS is able to induce a cleavage resynthesis cycle in stalled elongation complexes (resulting from the next missing nucleotide or a reduced incorporation rate of a wrong nucleotide) preventing misincorporation and enabling proofreading in a post-incorporation manner. Pausing of elongation complexes is the main determinant of TFS-induced RNA cleavage.
Family
Belongs to the archaeal RpoM/eukaryotic RPA12/RPB9/RPC11 RNA polymerase family.
Species
Archaeoglobus fulgidus (strain ATCC 49558 / VC-16 / DSM 4304 / JCM 9628 / NBRC 100126)
Length
103 amino acids
Sequence
MEFCPKCKSLMIYQGDKLVCRKCGYEKEADDSEELVIKVERNKEDVPVIEGENLKTLPTTKAICPACGHNEAFWWLRQLRAADESEVRFFRCTKCGKTWREYD
Mass
12.1 kDa
Simulated SDS-PAGE
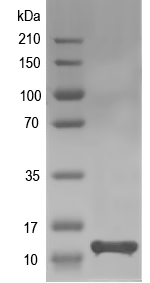 (Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)
(Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)Safety
Upon ordering, we will perform rigorous biosecurity and export control screening to ensure that order fulfillment is consistent with all legal and regulatory guidance.
Protein synthesis service
Make tfs using our protein expression services starting at $99 + $.30/amino acid in as fast as two weeks (includes the cost of DNA synthesis)
Order Here