Protein expression services for MAFF | Transcription factor MafF
Description
Since they lack a putative transactivation domain, the small Mafs behave as transcriptional repressors when they dimerize among themselves. However, they seem to serve as transcriptional activators by dimerizing with other (usually larger) basic-zipper proteins, such as NFE2L1/NRF1, and recruiting them to specific DNA-binding sites. Interacts with the upstream promoter region of the oxytocin receptor gene. May be a transcriptional enhancer in the up-regulation of the oxytocin receptor gene at parturition.
Family
Belongs to the bZIP family. Maf subfamily.
Species
Bos taurus
Length
172 amino acids
Sequence
MSVDPLSSKALKIKRELSENTPHLSDEALMGLSVRELNRHLRGLSAEEVTRLKQRRRTLKNRGYAASCRVKRVCQKEELQKQKSELEREVDKLARENAAMRLELDALRGKCEALQGFARSVAAARGPAALVAPASVITIVKSAPSPGPGPAPGPGPASGPGPAPGPAPAACS
Mass
18.2 kDa
Simulated SDS-PAGE
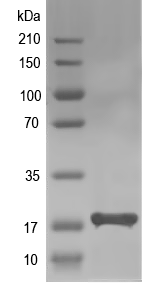 (Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)
(Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)Safety
Upon ordering, we will perform rigorous biosecurity and export control screening to ensure that order fulfillment is consistent with all legal and regulatory guidance.
Protein synthesis service
Make MAFF using our protein expression services starting at $99 + $.30/amino acid in as fast as two weeks (includes the cost of DNA synthesis)
Order Here