Protein expression services for motX | Sodium-type polar flagellar protein MotX
Description
The power to drive the polar flagellar rotary motor of V.parahaemolyticus is derived from the transmembrane potential of sodium ions. Force is generated by the motor on coupling of the movement of ions across the membrane to rotation of the flagellum. MotX interacts with MotY, which is the presumed stationary component of the motor. MotX may form a sodium channel.
Species
Vibrio parahaemolyticus serotype O3:K6 (strain RIMD 2210633)
Length
211 amino acids
Sequence
MKLRTVAASLLLMLSATTVRASAADVGAPVPIYTEAELIKLIEQNKHLQRVRADNCQLVEDIVARATRINLPAYEFLYGDMLAWGVCVEQDVELGLYYMENAAQQGLPAALEQIGRYYSRGTLVQQDKERAIPYLREAASMGNLNARIHLAELLLRDYGSPLDYEDAYRWLYNSVTADQRQHKRIAVLRRGLEQRMPQNIVARAKRRDMFW
Mass
24.1 kDa
Simulated SDS-PAGE
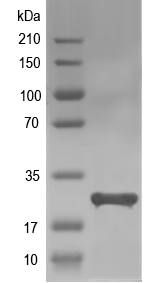 (Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)
(Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)Safety
Upon ordering, we will perform rigorous biosecurity and export control screening to ensure that order fulfillment is consistent with all legal and regulatory guidance.
Protein synthesis service
Make motX using our protein expression services starting at $99 + $.30/amino acid in as fast as two weeks (includes the cost of DNA synthesis)
Order Here