Protein expression services for SCT | Secretin
Description
Hormone involved in different processes, such as regulation of the pH of the duodenal content, food intake and water homeostasis. Exerts its biological effects by binding to secretin receptor (SCTR), a G-protein coupled receptor expressed in the basolateral domain of several cells. Acts as a key gastrointestinal hormone by regulating the pH of the duodenal content. Secreted by S cells of the duodenum in the crypts of Lieberkuehn and regulates the pH of the duodenum by (1) inhibiting the secretion of gastric acid from the parietal cells of the stomach and (2) stimulating the production of bicarbonate (NaHCO(3)) from the ductal cells of the pancreas (By similarity). Production of bicarbonate is essential to neutralize the pH and ensure no damage is done to the small intestine by the gastric acid. In addition to regulating the pH of the duodenal content, plays a central role in diet induced thermogenesis: acts as a non-sympathetic brown fat (BAT) activator mediating prandial thermogenesis, which consequentially induces satiation. Mechanistically, secretin released by the gut after a meal binds to secretin receptor (SCTR) in brown adipocytes, activating brown fat thermogenesis by stimulating lipolysis, which is sensed in the brain and promotes satiation. Also able to stimulate lipolysis in white adipocytes (By similarity). Also plays an important role in cellular osmoregulation: released into the systemic circulation in response to hyperosmolality and acts at different levels in the hypothalamus, pituitary and kidney to regulate water homeostasis (By similarity). Also plays a role in the central nervous system, possibly by acting as a neuropeptide hormone: required for hippocampal synaptic function and neural progenitor cells maintenance (By similarity).
Family
Belongs to the glucagon family.
Species
Sus scrofa
Length
134 amino acids
Sequence
MATRALLLLLLLPPLLLLAGCAARPAPPRAPRHSDGTFTSELSRLRDSARLQRLLQGLVGKRSQQDPENNTAWTKSGEDRLCQLWSHMPALQAWMPMKPPVDQAWSPWLPPGLRAGALVSEPAIPAAEGSPMPP
Mass
14.6 kDa
Simulated SDS-PAGE
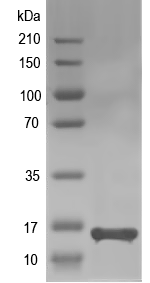 (Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)
(Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)Safety
Upon ordering, we will perform rigorous biosecurity and export control screening to ensure that order fulfillment is consistent with all legal and regulatory guidance.
Protein synthesis service
Make SCT using our protein expression services starting at $99 + $.30/amino acid in as fast as two weeks (includes the cost of DNA synthesis)
Order Here