Protein expression services for Nupr1 | Nuclear protein 1
Description
Transcription regulator that converts stress signals into a program of gene expression that empowers cells with resistance to the stress induced by a change in their microenvironment. Thereby participates in regulation of many process namely cell-cycle, apoptosis, autophagy and DNA repair responses (PubMed:27031958, PubMed:28694771, PubMed:20181828). Controls cell cycle progression and protects cells from genotoxic stress induced by doxorubicin through the complex formation with TP53 and EP300 that binds CDKN1A promoter leading to transcriptional induction of CDKN1A (By similarity). Protects pancreatic cancer cells from stress-induced cell death by binding the RELB promoter and activating its transcription, leading to IER3 transactivation (By similarity). Negatively regulates apoptosis through interaction with PTMA (By similarity). Inhibits autophagy-induced apoptosis in cardiac cells through FOXO3 interaction, inducing cytoplasmic translocation of FOXO3 thereby preventing the FOXO3 association with the pro-autophagic BNIP3 promoter (PubMed:20181828). Inhibits cell growth and facilitates programmed cell death by apoptosis after adriamycin-induced DNA damage through transactivation of TP53 (By similarity). Regulates methamphetamine-induced apoptosis and autophagy through DDIT3-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway (PubMed:28694771, PubMed:27031958). Participates to DNA repair following gamma-irradiation by facilitating DNA access of the transcription machinery through interaction with MSL1 leading to inhibition of histone H4' Lys-16' acetylation (H4K16ac) (By similarity). Coactivator of PAX2 transcription factor activity, both by recruiting the EP300 cofactor to increase PAX2 transcription factor activity and by binding PAXIP1 to suppress PAXIP1-induced inhibition on PAX2 (By similarity). Positively regulates cell cycle progression through interaction with COPS5 inducing cytoplasmic translocation of CDKN1B leading to the CDKN1B degradation (By similarity). Coordinates, through its interaction with EP300, the assiociation of MYOD1, EP300 and DDX5 to the MYOG promoter, leading to inhibition of cell-cycle progression and myogenic differentiation promotion (By similarity). Negatively regulates beta cell proliferation via inhibition of cell-cycle regulatory genes expression through the suppression of their promoter activities (By similarity). Also required for LHB expression and ovarian maturation (By similarity). Exacerbates CNS inflammation and demyelination upon cuprizone treatment (By similarity).
Family
Belongs to the NUPR family.
Species
Rattus norvegicus
Length
80 amino acids
Sequence
MATLPPTAHTSQQPVNIEDEDGILDEYDQYSLAQSYVVGGGRKGRTKREAAANTNRPSPGGHERKLLTKFQNSERKKAWR
Mass
9 kDa
Simulated SDS-PAGE
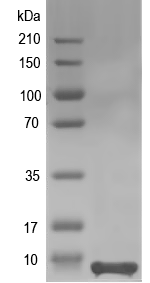 (Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)
(Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)Safety
Upon ordering, we will perform rigorous biosecurity and export control screening to ensure that order fulfillment is consistent with all legal and regulatory guidance.
Protein synthesis service
Make Nupr1 using our protein expression services starting at $99 + $.30/amino acid in as fast as two weeks (includes the cost of DNA synthesis)
Order Here