Protein expression services for Nfkb1 | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit
Description
NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52 and the heterodimeric p65-p50 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric p65-p50 and RelB-p50 complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kappa-B p50-p50 homodimer is a transcriptional repressor, but can act as a transcriptional activator when associated with BCL3. NFKB1 appears to have dual functions such as cytoplasmic retention of attached NF-kappa-B proteins by p105 and generation of p50 by a cotranslational processing. The proteasome-mediated process ensures the production of both p50 and p105 and preserves their independent function, although processing of NFKB1/p105 also appears to occur post-translationally. p50 binds to the kappa-B consensus sequence 5'-GGRNNYYCC-3', located in the enhancer region of genes involved in immune response and acute phase reactions. Plays a role in the regulation of apoptosis. Isoform 5, isoform 6 and isoform 7 act as inhibitors of transactivation of p50 NF-kappa-B subunit, probably by sequestering it in the cytoplasm. Isoform 3 (p98) (but not p84 or p105) acts as a transactivator of NF-kappa-B-regulated gene expression. In a complex with MAP3K8, NFKB1/p105 represses MAP3K8-induced MAPK signaling; active MAP3K8 is released by proteasome-dependent degradation of NFKB1/p105 (By similarity).
Species
Rattus norvegicus
Fragment
single
Length
522 amino acids
Sequence
REILNPPEKETQGEGPSLFMASTKTEAIAPASTMEDKEEDVGFQDNLFLEKALQLAKRHANALFDYAVTGDVKMLLAVQRHLTAVQDENGDSVLHLAIIHLHAQLVRDLLEVTSGSISDDIINMRNDLYQTPLHLAVITKQEDVVEDLLRVGADLSLLDRWGNSVLHLAAKEGHDKILGVLLKNSKAALLINHPNGEGLNAIHIAVMSNSLSCLQLLVAAGAEVNAQEQKSGRTALHLAVEYDNISLAGCLLLEGDALVDSTTYDGTTPLHIAAGRGSTRLAALLKAAGADPLVENFEPLYDLDDSWEKAGEDEGVVPGTTPLDMAANWQVFDILNGKPYEPVFTSDDILPQGDIKQLTEDTRLQLCKLLEIPDPDKNWATLAQKLGLGILNNAFRLSPAPSKTLMDNYEVSGGTIKELVEALRQMGYTEAIEVIQAAFRTPETTASSPVTTAQAHLLPLSSSSTRQHIDELRDNDSVCDSGVETSFRKLSFSESLTGDGPLLSLNKMPHNYGQDGPIEGKI
Mass
56.6 kDa
Simulated SDS-PAGE
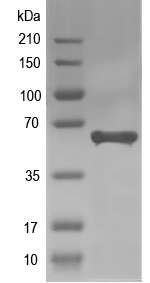 (Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)
(Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)Safety
Upon ordering, we will perform rigorous biosecurity and export control screening to ensure that order fulfillment is consistent with all legal and regulatory guidance.
Protein synthesis service
Make Nfkb1 using our protein expression services starting at $99 + $.30/amino acid in as fast as two weeks (includes the cost of DNA synthesis)
Order Here