Protein expression services for MIMI_R617 | N-glycosidase R617
Description
Catalyzes the hydrolysis of the N-glycosidic bond in the first two intermediates of riboflavin biosynthesis, which are highly reactive metabolites, yielding relatively innocuous products. Thus, can divert a surplus of harmful intermediates into relatively harmless products and pre-empt the damage these intermediates would otherwise do. May act on other substrates in vivo.
Family
Belongs to the YbiA family.
Species
Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus
Length
170 amino acids
Sequence
METDKYVFFHGANKNQAGVHIFSQWFPVNFKEYLNGEEFAEYVSAEQYMMAHKALLFGDMFHFKKIMECSKQCKIKYLGRRVRNFNPTIWDKHKFDIVTEGNRLKFSQNPDLMKRLLETGNKTIVEASPSDKIWGIGLTAQQAVNIPENKWPGKNLLGKVLMKIREENQQ
Mass
19.9 kDa
Simulated SDS-PAGE
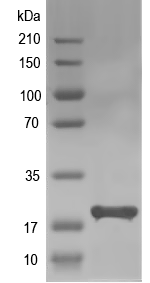 (Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)
(Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)Safety
Upon ordering, we will perform rigorous biosecurity and export control screening to ensure that order fulfillment is consistent with all legal and regulatory guidance.
Protein synthesis service
Make MIMI_R617 using our protein expression services starting at $99 + $.30/amino acid in as fast as two weeks (includes the cost of DNA synthesis)
Order Here