Protein expression services for msmC | Methanesulfonate monooxygenase ferredoxin subunit
Description
Methanesulfonate monooxygenase (MSAMO) mediates the primary degradation of methanesulfonic acid (MSA) to produce formaldehyd and inorganic sulfite by initial hydroxylation of the carbon atom prior to spontaneous cleavage of the unstable hydroxymethanesulfonic acid. MSAMO has a restricted substrate range that includes only the short-chain aliphatic sulfonates (methane- to butanesulfonate) and excludes all larger molecules, such as arylsulfonates and aromatic sulfonates. All MSAMO components are required for enzyme activity.
Family
Belongs to the bacterial ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase ferredoxin component family.
Species
Methylosulfonomonas methylovora
Length
123 amino acids
Sequence
MSWTYLCDAADVAPNSLKLVDANDIRVVVANYGSGFRAIPPICPHMEEPLDESGVIANCVLTCTKHLWAWNLISLELLGETEKPLKTYELKEEDGKLLAFIAEELTYDFEEEDDMDDDFFSKS
Mass
13.9 kDa
Simulated SDS-PAGE
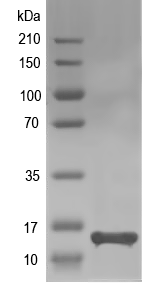 (Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)
(Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)Safety
Upon ordering, we will perform rigorous biosecurity and export control screening to ensure that order fulfillment is consistent with all legal and regulatory guidance.
Protein synthesis service
Make msmC using our protein expression services starting at $99 + $.30/amino acid in as fast as two weeks (includes the cost of DNA synthesis)
Order Here