Protein expression services for Katna1 | Katanin p60 ATPase-containing subunit A1
Description
Catalytic subunit of a complex which severs microtubules in an ATP-dependent manner. Microtubule severing may promote rapid reorganization of cellular microtubule arrays and the release of microtubules from the centrosome following nucleation. Microtubule release from the mitotic spindle poles may allow depolymerization of the microtubule end proximal to the spindle pole, leading to poleward microtubule flux and poleward motion of chromosome. The function in regulating microtubule dynamics at spindle poles seems to depend on the association of the katanin KATNA1:KATNB1 complex with ASPM which recruits it to microtubules. Reversely KATNA1:KATNB1 can enhance ASPM blocking activity on microtubule minus-end growth. Microtubule release within the cell body of neurons may be required for their transport into neuronal processes by microtubule-dependent motor proteins. This transport is required for axonal growth.
Family
Belongs to the AAA ATPase family. Katanin p60 subunit A1 subfamily.
Species
Mus musculus
Length
491 amino acids
Sequence
MSLQMIVENVKLAREYALLGNYDSAMVYYQGVLDQMNKYLYSVKDTHLRQKWQQVWQEINVEAKQVKDIMKTLESFKLDITSLQAAQHELPAAEGEVWSLPVPVERRPLPGPRKRQSSQHSDPKPHSNRPSTVVRAHRPSPQNLHNDRGKAVRSREKKEQSKGREEKNKLPAAVTEPEANKFDGTGYDKDLVEALERDIISQNPNVRWYDIADLVEAKKLLQEAVVLPMWMPEFFKGIRRPWKGVLMVGPPGTGKTLLAKAVATECKTTFFNVSSSTLTSKYRGESEKLVRLLFEMARFYSPATIFIDEIDSICSRRGTSEEHEASRRMKAELLVQMDGVGGASENDDPSKMVMVLAATNFPWDIDEALRRRLEKRIYIPLPSAKGREELLRISLRELELADDVNLASIAENMEGYSGADITNVCRDASLMAMRRRIEGLTPEEIRNLSREAMHMPTTMEDFEMALKKISKSVSAADIERYEKWIVEFGSC
Mass
55.9 kDa
Simulated SDS-PAGE
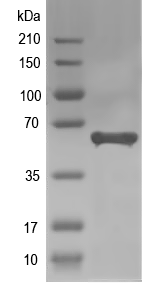 (Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)
(Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)Safety
Upon ordering, we will perform rigorous biosecurity and export control screening to ensure that order fulfillment is consistent with all legal and regulatory guidance.
Protein synthesis service
Make Katna1 using our protein expression services starting at $99 + $.30/amino acid in as fast as two weeks (includes the cost of DNA synthesis)
Order Here