Protein expression services for dhaA | Haloalkane dehalogenase
Description
Catalyzes hydrolytic cleavage of carbon-halogen bonds in halogenated aliphatic compounds, leading to the formation of the corresponding primary alcohols, halide ions and protons. Has a broad substrate specificity, as it is able to dehalogenate mono- and di- chlorinated and brominated alkanes (up to at least C10), and the two isomers of 1,3-dichloropropene to 3-chloroallyl alcohol; the highest activity was found with 1,2-dibromoethane, while no activity was observed with the analog 1,2-dichloroethane.
Family
Belongs to the haloalkane dehalogenase family. Type 2 subfamily.
Species
Pseudomonas pavonaceae
Length
293 amino acids
Sequence
MSEIGTGFPFDPHYVEVLGERMHYVDVGPRDGTPVLFLHGNPTSSYLWRNIIPHVAPSHRCIAPDLIGMGKSDKPDLDYFFDDHVRYLDAFIEALGLEEVVLVIHDWGSALGFHWAKRNPERVKGIACMEFIRPIPTWDEWPEFARETFQAFRTADVGRELIIDQNAFIEGALPKCVVRPLTEVEMDHYREPFLKPVDREPLWRFPNELPIAGEPANIVALVEAYMNWLHQSPVPKLLFWGTPGVLIPPAEAARLAESLPNCKTVDIGPGLHYLQEDNPDLIGSEIARWLPAL
Mass
33.2 kDa
Simulated SDS-PAGE
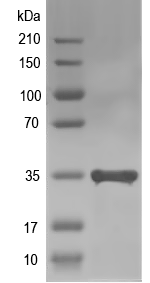 (Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)
(Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)Safety
Upon ordering, we will perform rigorous biosecurity and export control screening to ensure that order fulfillment is consistent with all legal and regulatory guidance.
Protein synthesis service
Make dhaA using our protein expression services starting at $99 + $.30/amino acid in as fast as two weeks (includes the cost of DNA synthesis)
Order Here