Protein expression services for NTHL1 | Endonuclease III-like protein 1
Description
Bifunctional DNA N-glycosylase with associated apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) lyase function that catalyzes the first step in base excision repair (BER), the primary repair pathway for the repair of oxidative DNA damage. The DNA N-glycosylase activity releases the damaged DNA base from DNA by cleaving the N-glycosidic bond, leaving an AP site. The AP-lyase activity cleaves the phosphodiester bond 3' to the AP site by a beta-elimination. Primarily recognizes and repairs oxidative base damage of pyrimidines. Has also 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-oxoG) DNA glycosylase activity. Acts preferentially on DNA damage opposite guanine residues in DNA. Is able to process lesions in nucleosomes without requiring or inducing nucleosome disruption.
Family
Belongs to the Nth/MutY family.
Species
Homo sapiens
Length
312 amino acids
Sequence
MCSPQESGMTALSARMLTRSRSLGPGAGPRGCREEPGPLRRREAAAEARKSHSPVKRPRKAQRLRVAYEGSDSEKGEGAEPLKVPVWEPQDWQQQLVNIRAMRNKKDAPVDHLGTEHCYDSSAPPKVRRYQVLLSLMLSSQTKDQVTAGAMQRLRARGLTVDSILQTDDATLGKLIYPVGFWRSKVKYIKQTSAILQQHYGGDIPASVAELVALPGVGPKMAHLAMAVAWGTVSGIAVDTHVHRIANRLRWTKKATKSPEETRAALEEWLPRELWHEINGLLVGFGQQTCLPVHPRCHACLNQALCPAAQGL
Mass
34.4 kDa
Simulated SDS-PAGE
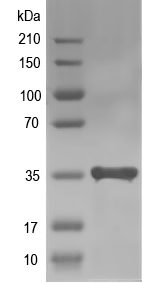 (Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)
(Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)Safety
Upon ordering, we will perform rigorous biosecurity and export control screening to ensure that order fulfillment is consistent with all legal and regulatory guidance.
Protein synthesis service
Make NTHL1 using our protein expression services starting at $99 + $.30/amino acid in as fast as two weeks (includes the cost of DNA synthesis)
Order Here