Protein expression services for hly | Alpha-hemolysin
Description
Alpha-toxin binds to the membrane of eukaryotic cells (particularly red blood cells, RBC) forming pores, resulting in hemolysis, with the release of low-molecular weight molecules leading to eventual osmotic RBC lysis. Human RBCs bind much less alpha-toxin than do rabbit RBCs (PubMed:1587866). Heptamer oligomerization and pore formation is required for lytic activity.
Family
Belongs to the aerolysin family.
Species
Staphylococcus aureus
Length
319 amino acids
Sequence
MKTRIVSSVTTTLLLGSILMNPVAGAADSDINIKTGTTDIGSNTTVKTGDLVTYDKENGMHKKVFYSFIDDKNHNKKLLVIRTKGTIAGQYRVYSEEGANKSGLAWPSAFKVQLQLPDNEVAQISDYYPRNSIDTKEYMSTLTYGFNGNVTGDDTGKIGGLIGANVSIGHTLKYVQPDFKTILESPTDKKVGWKVIFNNMVNQNWGPYDRDSWNPVYGNQLFMKTRNGSMKAADNFLDPNKASSLLSSGFSPDFATVITMDRKASKQQTNIDVIYERVRDDYQLHWTSTNWKGTNTKDKWTDRSSERYKIDWEKEEMTN
Mass
35.9 kDa
Simulated SDS-PAGE
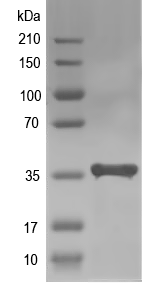 (Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)
(Note: Representative image - actual molecular weight may vary depending on tag type and expression method)Safety
Upon ordering, we will perform rigorous biosecurity and export control screening to ensure that order fulfillment is consistent with all legal and regulatory guidance.
Protein synthesis service
Make hly using our protein expression services starting at $99 + $.30/amino acid in as fast as two weeks (includes the cost of DNA synthesis)
Order Here